React-基础
React-基础
[扩展]
环境配置
创建项目
Create-React-App 创建, 官网推荐, 比较稳定
- 安装
如果不加 --template typescript 项目会默认使用 javascript
npx create-react-app my-app --template typescript
- 进入到目录中, 运行项目即可
npm start
- 安装
prettier规范代码风格
npm install prettier eslit-config-prettier eslint-plugin-prettier --save-dev
Vite 创建
- 安装
npm create vite@latest react-dome-vite --template react-ts
- 进行目录, 安装依赖
npm install
- 运行
npm run dev
代码规则
高质量代码的特点
- 严格编码规范(靠工具、流程,而非自觉)
- 合理、规范的注释
- 代码合理拆分
两者区别
eslint prettier
- eslint 编码规范,如变量未定义(语法语义)
- prettier 编码风格,如末尾是否用
; - eslint 也有编码风格的功能,两者可能会有冲突
eslint
安装插件
npm install eslint @typescript-eslint/parser @typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin -save-dev
初始化配置文件 .eslint.js
// .eslint.js
module.exports = {
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true,
},
extends: [
"eslint: recommended",
"plugin: react/recommended",
"plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended",
"plugin:prettier/recommended",
],
overrides: [],
parser: "@typescript-eslint/parser",
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: "latest",
sourceType: "module",
},
plugins: ["react", "atypescript-eslint"],
rules: {},
};
npx eslint --init ## 然后根据引导一步一步走
解释:eslint plugin 与 extend 的区别:
extend提供的是 eslint 现有规则的一系列预设plugin则提供了除预设之外的自定义规则,当你在 eslint 的规则里找不到合适的的时候就可以借用插件来实现了
安装 vscode 插件 eslint ,此时就可以看到代码 App.txs 中的错误提示(如定义一个未使用的变量)
在 package.json 中增加 scripts "lint": " eslint 'src/**/*.+(js|ts|jsx|tsx)' "
控制台运行 npm run lint 也可以看到错误提示。如果要自动修复,可以加 --fix 参数
prettier
npm install prettier eslint-config-prettier eslint-plugin-prettier -save-dev
eslint-config-prettier禁用所有和 Prettier 产生冲突的规则eslint-plugin-prettier把 Prettier 应用到 Eslint,配合 rules"prettier/prettier": "error"实现 Eslint 提醒。
在 eslint 配置文件的 extends 最后 增加 'plugin:prettier/recommended'
安装 vscode 插件 prettier ,此时可以看到代码 App.txs 中的格式提示(如末尾是否使用 ; ,或单引号、双引号)
在 package.json 中增加 scripts "format": " prettier --write 'src/**/*.+(js|ts|jsx|tsx)' "
控制台运行 npm run format 可以修复所有的格式错误
设置 vscode .vscode/settings.json 自动保存格式,可以在文件保存时,自动保留格式
{
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll.eslint": true
}
}
增加配置文件 .prettierrc.js 规定自己的编码格式,运行 npm run format 可以看到效果,保存文件也可以看到效果。
【注意】如果此处没效果,可以重启 vscode 再重试。
一直搞不定,重启 vscode 就好了。
在 vscode 搜“prettier” 插件时,发现一个 “reload required” 的提示,于是就重启了
CRA 创建的项目,配置文件是 js 格式
vite 创建的项目,配置文件是 cjs 格式
JSX
JSX 与 标签的区别
- 首字母大小写的区分,大写是自定义组件
- 每段 JSX 只能有一个根节点 (其中为
<></>空标签,空标签无法添加class等修饰)
return (
<>
<div>hello world</div>
</>
)
JSX 的属性
- 类型的变化,
class在 react 中需要写成className
return (
<div className="App">hello world</div>
)
为什么?
因为 JSX 是写在 ts 或者 js 中的,那么 class 已经是一个关键字了 (类)
所以,只能将名称改为 className
style要使用 JS 对象 (不能是string) 而且key用驼峰写法
错误写法
return (
<a style="color:red; background-color:white;"></a>
)
正确写法
return (
<a style={{ color: 'red', backgroundColor: 'white' }}></a>
)
[注意]
有两点需要注意
style必须用{}包起来并使用 对象的方式去写background-color这样的属性,只能在 css 中使用,JSX 或 TSX 需要写成这样backgroundColor,即采用 驼峰写法
- for 要改为 htmlFor
for 属性规定 label 与 哪个表单元素绑定,for 绑定的名称 与 表单 id 相同
<label for="male">Male</label>
<input type="radio" name="sex" id="male" />
JSX 中的写法
return (
<>
<label htmlFor="male">Male</label>
<input type="radio" name="sex" id="male" />
</>
)
JSX 中监听 DOM 事件
- 使用
onXxx的形式,定义事件
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
console.log('clicked')
}}
>
click
</button>
</div>
)
- 必须传入一个函数 ( 是fn 而非 fn() ,fn() 是执行结果, fn 才是一个函数)
const fn = () => {
console.log('clicked...')
}
return (
<div>
<button onClick={fn}>click</button>
</div>
)
JSX 函数传递 额外参数
const fn = (event: MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>, name: string) => {
event.preventDefault()
event.stopPropagation()
console.log('clicked...', name)
}
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={event => {
fn(event, 'Lin')
}}
>
click
</button>
</div>
)
JSX 中变量与表达式的插入
const style = { color: 'red', backgroundColor: 'white' }
return (
<div style={ style }>{ true ? 'true' : 'false' }</div>
)
JSX 中的注释
{/* 这个是注释 */}
JSX 中条件判断
简单使用
const flag = true
return (
<div>
<div>{flag && <p>Hello</p>}</div> {/* 单个元素的隐藏 */}
<div>{flag ? <p>Hello</p> : <p>你好</p>}</div> {/* 两个元素的要显示哪个一个 */}
</div>
)
函数的封装
function Hello() {
if (flag) return <p>hello1</p>
return <p>你好1</p>
}
return (
<div>
<Hello></Hello> {/* 首字母大写才是 自定义组件 */}
</div>
)
JSX 循环的使用
- 使用数组 map,来执行循环
- 每个 item 元素需要 key 属性
- key 在同级别唯一
- [注意] 不要使用 index 作为 key
const list = [
{ userName: 'shuangyue', name: '双越' },
{ userName: 'zhangsan', name: '张三' },
{ userName: 'lisi', name: '李四' },
]
return (
<ul>
{list.map(user => {
const { userName, name } = user
return <li key={userName}>{name}</li>
})}
</ul>
{/* 不要使用 index 作为 key,下面做法是错误的 */}
{/*<ul>
{list.map((user, index) => {
const { userName, name } = user
return <li key={index}>{name}</li>
})}
</ul>
*/}
)
JSX 与 Vue 设计理念的区别
判断 Vue 采用 v-if,React 使用 三元表达式,或者 &&
循环 Vue 采用 v-for,React 使用 map 进行循环,但是两者同样需要 key
React - 能用 js 的就用 js
Vue - 自定义很多指令,方便初学者学习和记忆
[注意]
Vue3 也能很好的支持 JSX 语法
JSX 中使用 html
dangerouslySetInnerHTML 属性能将 文本转换为 html
import React, { FC, useState, ChangeEvent } from 'react'
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [text, setText] = useState<string>('hello')
function handleChange(event: ChangeEvent<HTMLTextAreaElement>) {
setText(event.target.value)
}
function getHTML() {
return { __html: text.replaceAll('\n', '<br>') }
}
return (
<>
<div>
<textarea value={text} onChange={handleChange}></textarea>
<p dangerouslySetInnerHTML={getHTML()}></p> // 将文本转化为 html
</div>
</>
)
}
export default Demo
小结
标签
属性
事件
JS 变量或表达式
条件判断
循环
增、删、改、查
基本操作的语法
增加 concat
删除、查询 filter
修改 map
import React, { FC, useState } from 'react'
import QuestionCard from './components/QuestionCard'
const List2: FC = () => {
const [questionList, setQuestionList] = useState([
{ id: 'q1', title: '问卷1', isPublished: false },
{ id: 'q2', title: '问卷2', isPublished: true },
{ id: 'q3', title: '问卷3', isPublished: false },
{ id: 'q4', title: '问卷4', isPublished: true },
])
function add() {
const r = Math.random().toString().slice(-3)
setQuestionList(
// 添加 concat
questionList.concat({
id: 'qs' + r,
title: '问卷' + r,
isPublished: false,
})
)
}
function deleteQuestion(id: string) {
// 不可变数据
setQuestionList(
// 删除/查询 filter
questionList.filter(q => {
if (q.id === id) return false
else return true
})
)
}
function publishQuestion(id: string) {
setQuestionList(
// 修改 map
questionList.map(q => {
if (q.id !== id) return q
return {
...q,
isPublished: true,
}
})
)
}
return (
<div>
<h1>问卷列表页2</h1>
<div>
{questionList.map(question => {
const { id, title, isPublished } = question
return (
<QuestionCard
key={id}
id={id}
title={title}
isPublished={isPublished}
deleteQuestion={deleteQuestion}
publishQuestion={publishQuestion}
/>
)
})}
</div>
<div>
<button onClick={add}>新增问卷</button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default List2
immer
immer 是第三库,用来实现更方便的 增、删、改、查
增加 push
删除/查找 findIndex 、splice
修改 find,直接修改属性 .属性名
import React, { FC, useState } from 'react'
import QuestionCard from './components/QuestionCard'
import { produce } from 'immer'
const List2: FC = () => {
const [questionList, setQuestionList] = useState([
{ id: 'q1', title: '问卷1', isPublished: false },
{ id: 'q2', title: '问卷2', isPublished: true },
{ id: 'q3', title: '问卷3', isPublished: false },
{ id: 'q4', title: '问卷4', isPublished: true },
])
function add() {
const r = Math.random().toString().slice(-3)
// setQuestionList(
// // 添加 concat
// questionList.concat({
// id: 'qs' + r,
// title: '问卷' + r,
// isPublished: false,
// })
// )
// immer 增加
setQuestionList(
produce(draft => {
draft.push({
id: 'q' + r,
title: '问卷' + r,
isPublished: false,
})
})
)
}
function deleteQuestion(id: string) {
// 不可变数据
// setQuestionList(
// // 删除/查询 filter
// questionList.filter(q => {
// if (q.id === id) return false
// else return true
// })
// )
// immer 删除
setQuestionList(
produce(draft => {
const index = draft.findIndex(q => q.id === id)
draft.splice(index, 1)
})
)
}
function publishQuestion(id: string) {
// setQuestionList(
// // 修改 map
// questionList.map(q => {
// if (q.id !== id) return q
// return {
// ...q,
// isPublished: true,
// }
// })
// )
// immer 修改
setQuestionList(
produce(draft => {
const q = draft.find(item => item.id === id)
if (q) q.isPublished = true
})
)
}
return (
<div>
<h1>问卷列表页2</h1>
<div>
{questionList.map(question => {
const { id, title, isPublished } = question
return (
<QuestionCard
key={id}
id={id}
title={title}
isPublished={isPublished}
deleteQuestion={deleteQuestion}
publishQuestion={publishQuestion}
/>
)
})}
</div>
<div>
<button onClick={add}>新增问卷</button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default List2
Typescript 类型基础知识补充
<T> 泛型的使用
function print<T>(info: T) {
console.log(info)
}
print<string>('hello')
<T> 的含义就是等待类型被定义,也就是说可以在使用的时候再去定义类型
通常你在 typescript 中看到 <> 尖括号基本都是 泛型
class 中加 泛型
function print<T>(info: T) {
console.log(info)
}
print<string>('hello')
泛型定义一个数组
const arr: Array<string> = [] // 泛型定义 字符类型的数组
const arr: string[] = [] // 直接命名定义数组类型
TS 中获取一个类型
import type { MouseEvent } from 'react'
function App() {
const fn = (event: MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
event.preventDefault() // 阻止默认行为
}
}
上面的例子就是引入了类型 MouseEvent ,并且使用
函数返回值类型定义
function fn(): string {
return 'xx'
}
解构重命名
const [loading, run: handleCreateClick] = useRequest()
handleCreateClick() // 相当于 执行 run()
Partial 的妙用
定义复杂数据类型,可用 ?: 定义一些可能不必有的属性
这样是话,b、c 可有,也可无,都不会报错
type ObjType = {
a: string
b?: number
c?: boolean
}
const obj1: ObjType = {
a: 'x'
}
但是,如果要定义的复杂数据类型过多,那就显得不灵活啦
那么,有没有什么 API 语法可以简化呢,答案是有的,partial
partial 有部分的意思
也就是说有 partial 用这个关键字定义后,定义的数据,只需要有预先定义的复杂数据类型的一部分即可
type ObjType = {
a: string
b: number
c: boolean
}
const obj1: Partial<ObjType> = {
a: 'x'
}
组件 与 props
React 一切皆组件
- 组件就是一个 UI 片段
- 拥有独立的逻辑和显示
- 组件可大可小,可嵌套
react 有两种组件,class 组件 和 函数组件
React16 以后,React 推崇 函数组件 和 Hooks
组件是一个函数(执行放回 JSX 片段),组件初次渲染执行这个函数
任何 state 更新,都会触发组件的更新(重新执行函数)
Props.children
Props.children 类似于 Vue 中的 slot 插槽
// 父组件
return (
<Child>
<span>{ 'child node' }</span>
</Child>
)
// 子组件
return (
<div>
{ props.children }
</div>
)
状态提升
状态提升 state
数据源在父组件里面,每个子组件只需要执行父组件传过来的数据和方法,这就是 状态提升
Outlet
类似于 vue 中 slot 插槽
受控组件 与 非受控组件
- 受控组件:值同步到 state,使用 value 属性
- 非受控组件:值不同步 state,使用 defaultValue 属性
- React 推荐使用受控组件,看似繁琐,实则更加可控
Hooks
为什么 react 需要使用到 useState 这样的钩子函数呢
因为普通 js 变量,无法触发组件的更新,useState 可以触发这样的更新
触发条件就是使用,setCount 进行更新
import React, { useState } from 'react'
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
function add() {
setCount(count + 1)
}
// 列表页
return (
<>
<div>
<button onClick={add}>add {count}</button>
</div>
</>
)
}
export default App
state 有哪些特点?
- state 的更新是异步的,所以无法拿到最新的 state 值
[注意]
如果说一个变量 不用于 JSX 中显示,那就不要用 setState 来管理它 (因为 useState 会触发组件更新,所以没必要),用 useRef
- state 可能会被合并
add 函数执行结果一次的结果只加 1
因为,每次执行 setCount(count + 1) ,使用值进行更新,都被合并了
import React, { FC, useState } from 'react'
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
function add() {
setCount(count + 1)
setCount(count + 1)
setCount(count + 1)
setCount(count + 1)
setCount(count + 1)
// setCount(count => count + 1) setCount 的第二种写法
}
return (
<div>
<button onClick={add}>add {count}</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Demo
如果是使用函数来更新就不会被合并,因为函数是一个比较复杂的结构
add 函数执行结果一次的结果加 5
import React, { FC, useState } from 'react'
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
function add() {
setCount(count => count + 1)
setCount(count => count + 1)
setCount(count => count + 1)
setCount(count => count + 1)
setCount(count => count + 1)
// setCount(count => count + 1) setCount 的第二种写法
}
return (
<div>
<button onClick={add}>add {count}</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Demo
- 不可变数据 !!!
useEffect
useEffect 能监听组件的生命周期,创建、更新、销毁
函数是一个组件,useEffect 在函数中执行
- 只执行一次,数组中为空,只执行一次
谁引用了 List2,谁就执行 useEffect 一次
const List2: FC = () => {
useEffect(() => {
console.log('加载 ajax 网络请求')
}, [])
}
- 监听
useState数据变化
const List2: FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
useEffect(() => {
console.log('count change')
}, [count])
function add() {
setCount(count + 1)
}
}
- 监听函数 创建 与 销毁
useEffect(() => {
console.log('question card mounted') // 监听创建
return () => {
console.log('question card unmounted', id) // 监听销毁
}
})
[注]
useEffect 在开发环境下会执行两次?
先创建一次,销毁一次,再次创建
从 React 18 开始,useEffect 在开发环境下会执行两次
这样做的目的,模拟组件创建、销毁,再创建的完整流程,及早暴露问题
生产环境下会执行一次
useRef
一般用于操作 DOM
也可传入普通 JS 变量, 但更新不会触发 rerender
import React, { FC, useRef } from 'react'
const Demo: FC = () => {
const nameRef = useRef('lin')
function changeName() {
nameRef.current = 'linjk' // 修改 ref 值, 不会触发 rerender (state 修改组件会触发组件的 rerender)
}
return (
<>
<p>name {nameRef.current}</p>
<div>
<button onClick={changeName}>change name</button>
</div>
</>
)
}
export default Demo
useMemo
- 函数组件, 每次 state 更新都会重新执行函数
- useMemo 可以缓存数据, 不用每次执行函数都重新生成
- 可用于计算量较大的场景,缓存提高性能
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [num1, setNum1] = useState(10)
const [num2, setNum2] = useState(20)
const sum = useMemo(() => {
console.log('gen sum ...') // 缓存
return num1 + num2
}, [num1, num2])
}
useCallback
类似与 useDemo 同样是用来缓存组件
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [text, setText] = useState('hello')
const fn2 = useCallback(() => {
console.log('fn2 text:', text)
}, [text])
}
自定义 hooks
类似于,定义一个外部函数,可以引入使用
外部 hooks
// hooks/useTitle.ts
import { useEffect } from 'react'
function useTitle(title: string) {
useEffect(() => {
document.title = title
}, [])
}
export default useTitle
调用 hooks
// index.tsx
import React from 'react'
import useTitle from './hooks/useTitle'
function App() {
useTitle('App page 2')
return (
<>
<p>App page</p>
</>
)
}
export default App
- 自定义 hooks (获取鼠标位置)
外部 hooks
下面 mouseMoveHandler 每次执行这个函数都会创建一次,我们鼠标移动一次就会创建一次,可以使用 useCallback 进行缓存起来
比较大量的计算可以使用 useCallback,比较小的计算可以不同,根据具体情况而定
// hooks/useMouse.ts
import { useState, useEffect, useCallback } from 'react'
// 获取鼠标位置
function useMouse() {
const [x, setX] = useState(0)
const [y, setY] = useState(0)
const mouseMoveHandler = useCallback((event: MouseEvent) => {
setX(event.clientX)
setY(event.clientY)
}, [])
useEffect(() => {
// 监听鼠标事件
window.addEventListener('mousemove', mouseMoveHandler)
// 组件销毁时,一定要解绑 DOM 事件 !!! 可能出现内存泄漏问题
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', mouseMoveHandler)
}
}, [])
return { x, y }
}
export default useMouse
引用 hooks
// index.ts
import React from 'react'
import useMouse from './hooks/useMouse'
function App() {
const { x, y } = useMouse()
// 列表页
return (
<>
<p>
App page {x} {y}
</p>
</>
)
}
export default App
- 模拟 hooks 异步加载数据
外部 hooks
// hooks/getInfo.ts
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
function getInfo(): Promise<string> { // Promsie 模拟请求
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(Date.now().toString())
}, 1500)
})
}
const useGetInfo = () => {
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true)
const [info, setInfo] = useState('')
useEffect(() => {
getInfo().then(info => {
setLoading(false)
setInfo(info)
})
}, [])
return { loading, info }
}
export default useGetInfo
引用 hooks
import React from 'react'
import useGetInfo from './hooks/useGetInfo'
function App() {
const { loading, info } = useGetInfo()
return (
<>
<p>App page</p>
<p>{loading ? '加载中...' : info}</p>
</>
)
}
export default App
组件生命周期
函数组件的 销毁阶段
下面例子的组件销毁阶段,就在于 useEffect 中 return 返回的函数,就是组件销毁阶段要执行的东西
import { useState, useEffect, useCallback } from 'react'
// 获取鼠标位置
function useMouse() {
const [x, setX] = useState(0)
const [y, setY] = useState(0)
const mouseMoveHandler = useCallback((event: MouseEvent) => {
setX(event.clientX)
setY(event.clientY)
}, [])
useEffect(() => {
// 监听鼠标事件
window.addEventListener('mousemove', mouseMoveHandler)
// 组件销毁时,一定要解绑 DOM 事件 !!! 可能出现内存泄漏问题
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', mouseMoveHandler)
}
}, [])
return { x, y }
}
export default useMouse
第三方 Hooks 的使用
- 国内流行 ahooks
- 国外流行 React Hooks
ahooks 的使用案例,useTitle、useMouse 的使用
import React from 'react'
import { useTitle, useMouse } from 'ahooks'
function App() {
useTitle('App page 3')
const { clientX, clientY } = useMouse()
// 列表页
return (
<>
<p>App page</p>
{clientX} {clientY}
</>
)
}
export default App
Hooks 使用规则
- 必须用 useXxxx 格式来命名
- 只能在两个地方调用 Hook (组件内,其他 Hook 内)
- 必须保证每次的调用顺序一致 (不能放在 if for 内部)
Hooks 闭包陷阱
- 当异步函数获取 state 时,可能不是当前最新的 state
import React, { FC, useState } from 'react'
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
function add() {
setCount(count + 1)
}
function alertFn() {
setTimeout(() => {
alert(count) // count 5 闭包
}, 3000)
}
return (
<>
<p>闭包陷阱</p>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={add}>add</button>
<button onClick={alertFn}>alert</button>
</>
// 点击 alert 后,多次点击 add,弹窗出来的接口,不等于 count
// 也就所谓的 闭包陷阱
)
}
export default Demo
解决的办法,使用 useRef,因为它的值是引用类型,根据原值的改变而改变
原先用 useState 定的值是值类型,所以点击 alert 的时候,count 是 5 的话,那么弹窗的值也是 5
import React, { FC, useState, useRef, useEffect } from 'react'
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const countRef = useRef(0)
useEffect(() => {
countRef.current = count
}, [count])
function add() {
setCount(count + 1)
}
function alertFn() {
setTimeout(() => {
// alert(counr) // count 值类型
alert(countRef.current) // ref 引用类型
}, 3000)
}
return (
<>
<p>闭包陷阱</p>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={add}>add</button>
<button onClick={alertFn}>alert</button>
</>
// 点击 alert 后,多次点击 add,弹窗出来的接口,不等于 count
// 也就所谓的 闭包陷阱
)
}
export default Demo
CSS
内联样式条件判断怎么写
基础写法
const Demo: FC = () => {
let isPublished = true
let itemClassName = 'list-item'
if (isPublished) itemClassName += ' published'
return (
<div className={itemClassName}>
)
}
使用第三方插件 classnames 进行条件判断
const Demo: FC = () => {
let isPublished = true
const itemClassName = classnames('list-item', { published: isPublished })
const itemClassName = classnames({
'list-item': true,
published: isPublished,
})
return (
<div className={itemClassName}>
)
}
解决 clasName 可能重复的问题
使用 CSS Module 进行解决
- 每个 CSS 文件都当做单独的模块,命令
xxx.module.css - 为每个
className增加后缀名,不让它们重复 Create-React-App原生支持CSS Module
使用方法就是 将需要引入的 css 命名后缀 .css 改为 .module.css
那么在构建的是时候,就会为该组件的类名等,添加前后缀来进行区别!
CSS-in-JS
使用 js 的方式写 css
import React, { FC } from 'react'
import styled, { css } from 'styled-components'
// Button 组件
type ButtonPropsType = {
primary?: boolean // 定义属性类型
}
// 定义组件
const Button = styled.button`
background: transparent;
border-radius: 3px;
border: 2px solid palevioletred;
color: palevioletred;
margin: 0 1em;
padding: 0.25em 1em;
${(props: ButtonPropsType) =>
props.primary && // 当属性 primary 存在的时候,css 中的内容生效
css`
background: palevioletred;
color: white;
`}
`
// Container 组件,定义 div 的元素居中显示
const Container = styled.div`
text-align: center;
`
const Demo: FC = () => {
return (
<div>
<p>style-component</p>
<Container>
<Button>Normal Button</Button>
<Button primary>primary Button</Button>
</Container>
</div>
)
}
export default Demo
[注]
关于 div 这个语法的解释
div 类似一个函数执行
const Container = styled.div`
text-align: center;
`
可以看到 类似函数的调用,但是返回的是一个数组,且有一些属性信息
关于 flex 布局的写法
三列布局,两变固定大小,中间自适应
外层可以用 display: flex
中间层可以用 flex: auto
为了不让 中间 和 左右因为缩放被挤压,可以设置最小宽高 min-width、min-height
三列布局 按比例划分 3份, 中间 2 份,左右各一份
可以使用中间 flex: 2
左右使用 flex: 1
class 类有 横杠 如何写入 className
<div className={styles['component-wrapper']}>
<div className={styles.component}>
<QuestionInput placeholder={''} />
</div>
</div>
多个 className
// 动态判断添加单类名
<div className={detail.applyStatus == 1 ? styles.class : styles.class2 }>HELLO WORLD</div>
// 已有多类名,动态判断再添加类名
// ( 数组法)
<div className{[classA,'box',index===this.state.currentState?"active":null].join('')}>HELLO WORLD</div>
// (模板字符串法)
<div className={`box${classA}${index===this.state.currentState?"active":null}`}>HELLO WORLD</div>
一些特殊属性
// 屏蔽鼠标行为,组件不让被点击到
.component {
pointer-events: none;
}
// 动画 暂停 与 恢复
.container {
animation: rotate 20s linear infinite;
animation-play-state: paused;
}
.container: hover {
animation-play-state: running;
}
路由
路由跳转的三种方式
- 直接通过 函数的方式 跳转
import React, { FC } from 'react'
import { useNavigate } from 'react-router-dom'
const Home: FC = () => {
const nav = useNavigate()
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => nav(-1)}>返回</button> // 返回上一级
</div>
)
}
export default Home
- 通过
nav进行 跳转
import React, { FC } from 'react'
import { useNavigate } from 'react-router-dom'
const Home: FC = () => {
const nav = useNavigate()
function clickHandler() {
// nav('/login?b=20')
nav({
pathname: '/login',
search: 'b=21',
})
}
return (
<div>
<button onClick={clickHandler}>登录</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Home
- 通过
Link插件进行 跳转
import React, { FC } from 'react'
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom'
const Home: FC = () => {
return (
<div>
<Link to="/register?a=10">注册</Link>
</div>
)
}
export default Home
获取参数
- 获取动态路由的动态参数
import React, { FC } from 'react'
import { useParams } from 'react-router-dom' // 通过 useParams 获取
const Edit: FC = () => {
const { id = '' } = useParams()
return (
<>
<p>Edit {id}</p>
</>
)
}
export default Edit
- 获取当前
url的参数
import React, { FC } from 'react'
import { useSearchParams } from 'react-router-dom'
const List: FC = () => {
const [searchParams] = useSearchParams()
console.log('keyword', searchParams.get('keyword'))
return <></>
}
export default List
- 获取当前路由路径的方法
import { useLocation } from 'react-router-dom'
const ManageLayout: FC = () => {
const { pathname } = useLocation()
console.log('pathname', pathname) // /manage/list
return (
<Button
type={pathname.startsWith('/manage/list') ? 'default' : 'text'} // pathname.startsWith('/manage/list') 用于判断路径是匹配
size="large"
icon={<BarsOutlined rev={undefined} />}
onClick={() => nav('/manage/list')}
>
)
}
Mock
主要功能
mock.js 两大功能:劫持 Ajax + 全面的 Random 能力
把 mock.js 用于 nodejs 服务端,使用 Random 能力
应用场景
通常使用的话,主要使用另开一个服务运行 mockjs
如果使用原项目的话,请求路径被劫持,如果这个 mock 上线了,会导致相同的线上接口返回的是 mock 数据,而无法得到真实数据
重新写一个 mock 服务花不了多少时间,能重新开一个服务就开一个服务
跨域
使用 craco 进行跨域代理
具体使用方法
- 安装
npm i -D @craco/craco
- 使用方法、根目录下建一个
craco.config.js文件
// 根目录下建一个
module.exports = {
// common.js
devServer: {
proxy: {
'/api': 'http://localhost:3001',
},
},
}
Restful API
设计规范
- method 按照,对资源的操作类型,get、post、patch (或者 put 修改)、delete,进行操作
- path 按照,每个路径代表某一类资源,加上 id 就代表这一类资源
/api/question/:id
下面就 用户功能、问卷管理 的两个 Restful API 设计实例
用户功能
获取用户信息
- method
get - path
/api/user/info - response
{ errno: 0, data: {...} }或{ errno: 10001, msg: 'xxx' }
注册
- method
post - path
/api/user/register - request body
{ username, password, nickname } - response
{ errno: 0 }
登录
- method
post - path
/api/user/login - request body
{ username, password } - response
{ errno: 0, data: { token } }—— JWT 使用 token
问卷功能
创建问卷
- method
post - path
/api/question - request body - 无 (点击一个按钮即可创建,title 自动生成)
- response
{ errno: 0, data: { id } }
获取单个问卷
- method
get - path
/api/question/:id - response
{ errno: 0, data: { id, title ... } }
获取问卷列表
- method
get - path
/api/question - response:
{ errno: 0, data: { list: [ ... ], total } }
更新问卷信息
- method
patch - path
/api/question/:id - request body
{ title, isStar ... }(之前忘记了,现补上) - response:
{ errno: 0 }
PS:删除是假删除,实际是更新 isDeleted 属性
批量彻底删除问卷
- method
delete - path
/api/question - request body
{ ids: [ ... ] } - response:
{ errno: 0 }
复制问卷
- method
post - path
/api/question/duplicate/:id - response:
{ errno: 0, data: { id } }
JWT
简叙
中小型网站用于,用户登录,或者说用于 用户信息验证的一种方式
JWT (JSON Web Token)
登录成功之后,服务端返回一个 token (令牌,一段字符串)
以后每次请求都带这个 token, 以表明自己的身份
DOM 操作
场景
滚动到底部加载
实现
使用 useRef 进行操作
获取元素到顶部的距离 getBoundingClientRect
Element.getBoundingClientRect)
import React, { FC, useRef } from 'react'
import { useDebounceFn } from 'ahooks'
const List: FC = () => {
// 触发加载的函数 - 防抖
const containerRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null)
const { run: tryLoadMore } = useDebounceFn(
() => {
const elem = containerRef.current
if (elem == null) return
const domRect = elem.getBoundingClientRect() // 获取 底部元素到顶部的距离
if (domRect == null) return
const { bottom } = domRect
if (bottom <= document.body.clientHeight) { // document.body.clientHeight 获取 body 的高度
console.log('tryLoadMore...')
}
},
{
wait: 1000,
}
)
// 当页面加载,或者 url 参数 (keyword) 变化时,触发加载
useEffect(() => {
tryLoadMore() // 加载第一页
}, [searchParams])
return (
<>
<div className={styles.footer}>
<div ref={containerRef}>loadMore... 上划加载更多...</div>
</div>
</>
)
}
export default List
Context
实例
目录结构;
.
|-- ThemeButton.tsx
|-- Toolbar.tsx
`-- index.tsx
// 第一层 index.tsx
import React, { FC, createContext, useState } from 'react'
import { ThemeContext } from 'styled-components'
import Toolbar from './Toolbar'
const themes = {
light: {
fore: '#000',
background: '#eee',
},
dark: {
fore: '#fff',
background: '#222',
},
}
// 定义 ThemeContext
export const ThemeContect = createContext(themes.light)
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState(themes.light)
function toDark() {
setTheme(themes.dark)
}
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={theme}>
<div>
<div>
<span>Context Demo</span>
<button onClick={toDark}>dark</button>
</div>
</div>
<Toolbar />
</ThemeContext.Provider>
)
}
export default Demo
// 第二层 Toolbar.tsx
import React, { FC } from 'react'
import ThemeButton from './ThemeButton'
const Toolbar: FC = () => {
return (
<>
<p>Toolbar</p>
<div>
<ThemeButton />
</div>
</>
)
}
export default Toolbar
// 第三层 ThemeButton.tsx
import React, { FC, useContext } from 'react'
import { ThemeContext } from 'styled-components'
const ThemeButton: FC = () => {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext)
// 根据 theme 设置 button 样式
const style = { color: theme.fore, background: theme.background }
return <button style={style}>theme button</button>
}
export default ThemeButton
[注]
- 类似于 Vue 的 provide/inject
- 可跨层级传递,而不像 props 层层传递
- 场景:切换主题、切换语言 (场景比较单一)
useReduce
实例
import React, { FC, useReducer } from 'react'
type StateType = { count: number }
type ActionType = { type: string }
const initialState: StateType = { count: 100 } // 初始值
// 根据传入的 action 返回新的 state (不可变数据)
function reducer(state: StateType, action: ActionType) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment':
return { count: state.count + 1 }
case 'decrement':
return { count: state.count - 1 }
default:
throw new Error()
}
}
const CountReducer: FC = () => {
// const [count, setCount] = useState(100)
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState)
return (
<>
<span>count: {state.count}</span>
{/* <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count - 1)}>-</button> */}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'increment' })}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'decrement' })}>-</button>
</>
)
}
export default CountReducer
Redux
Redux 单向数据流
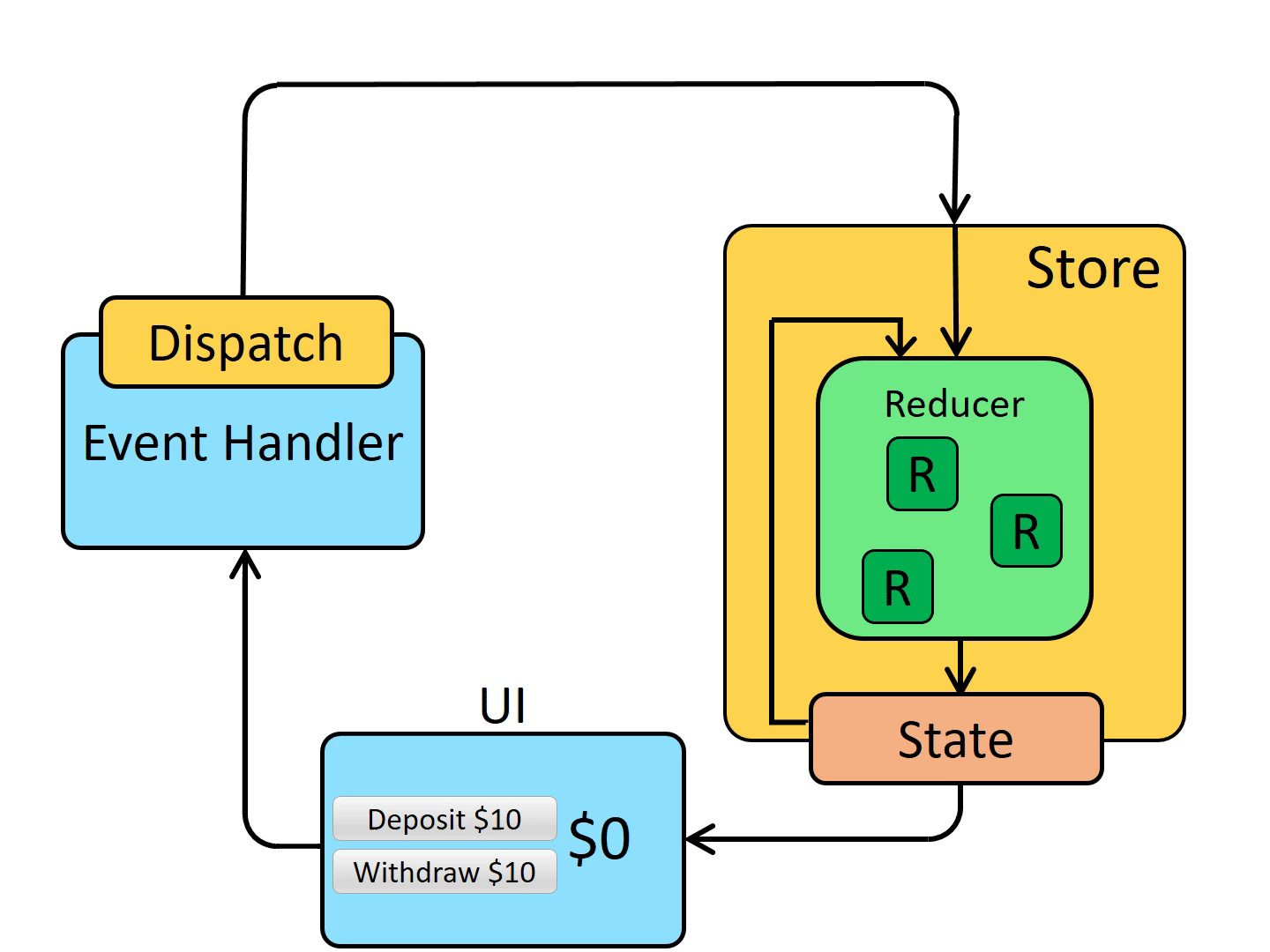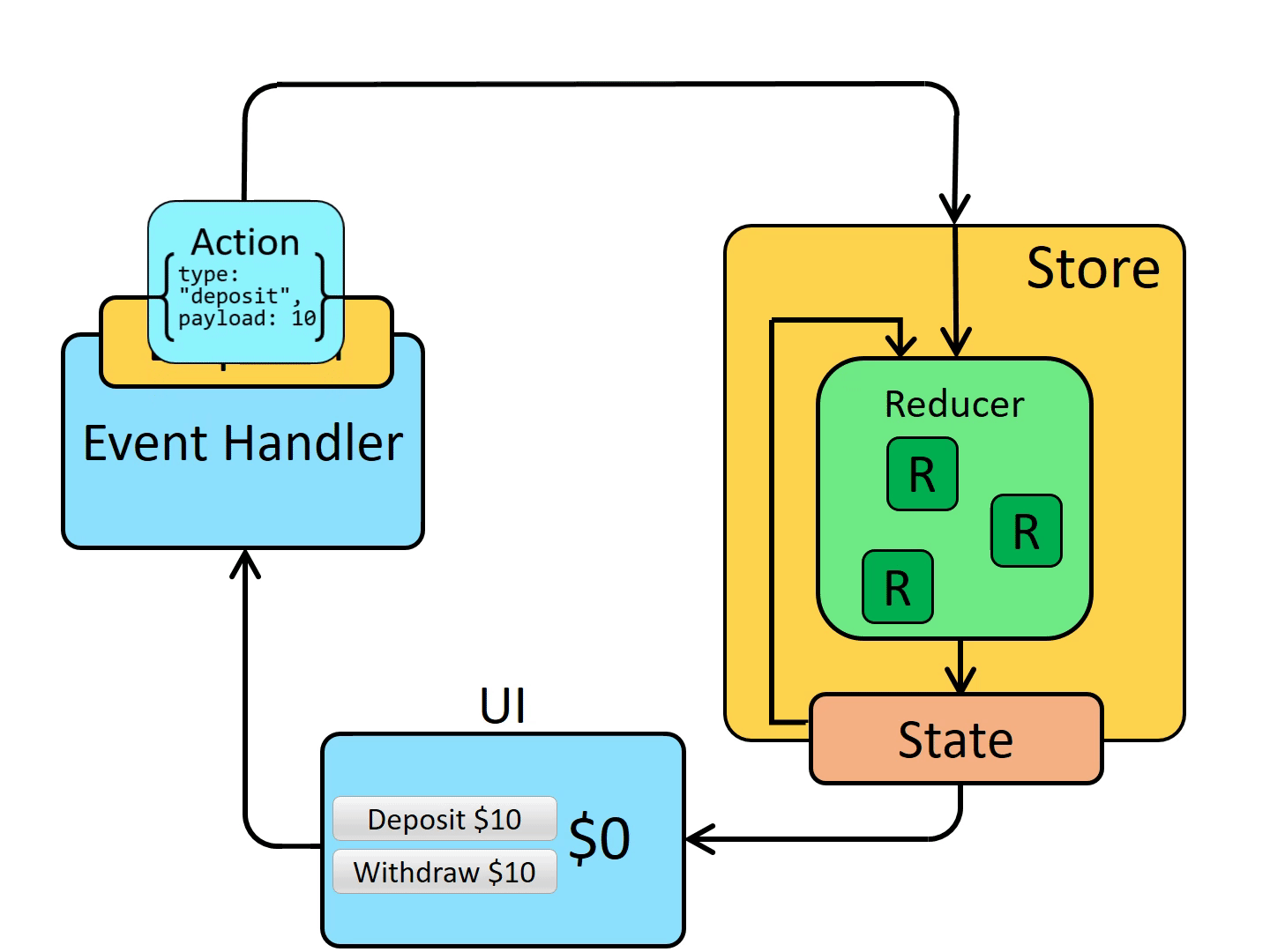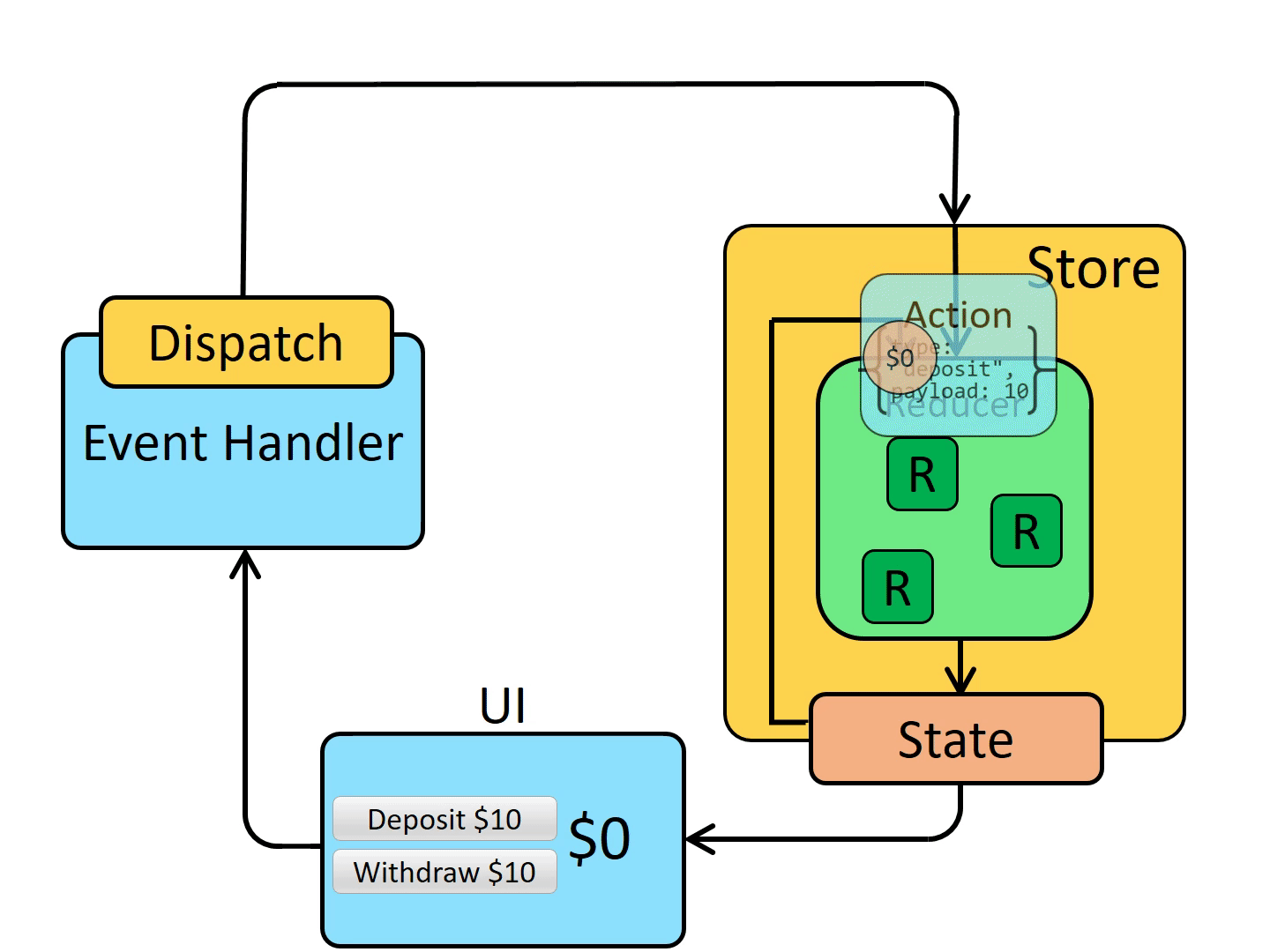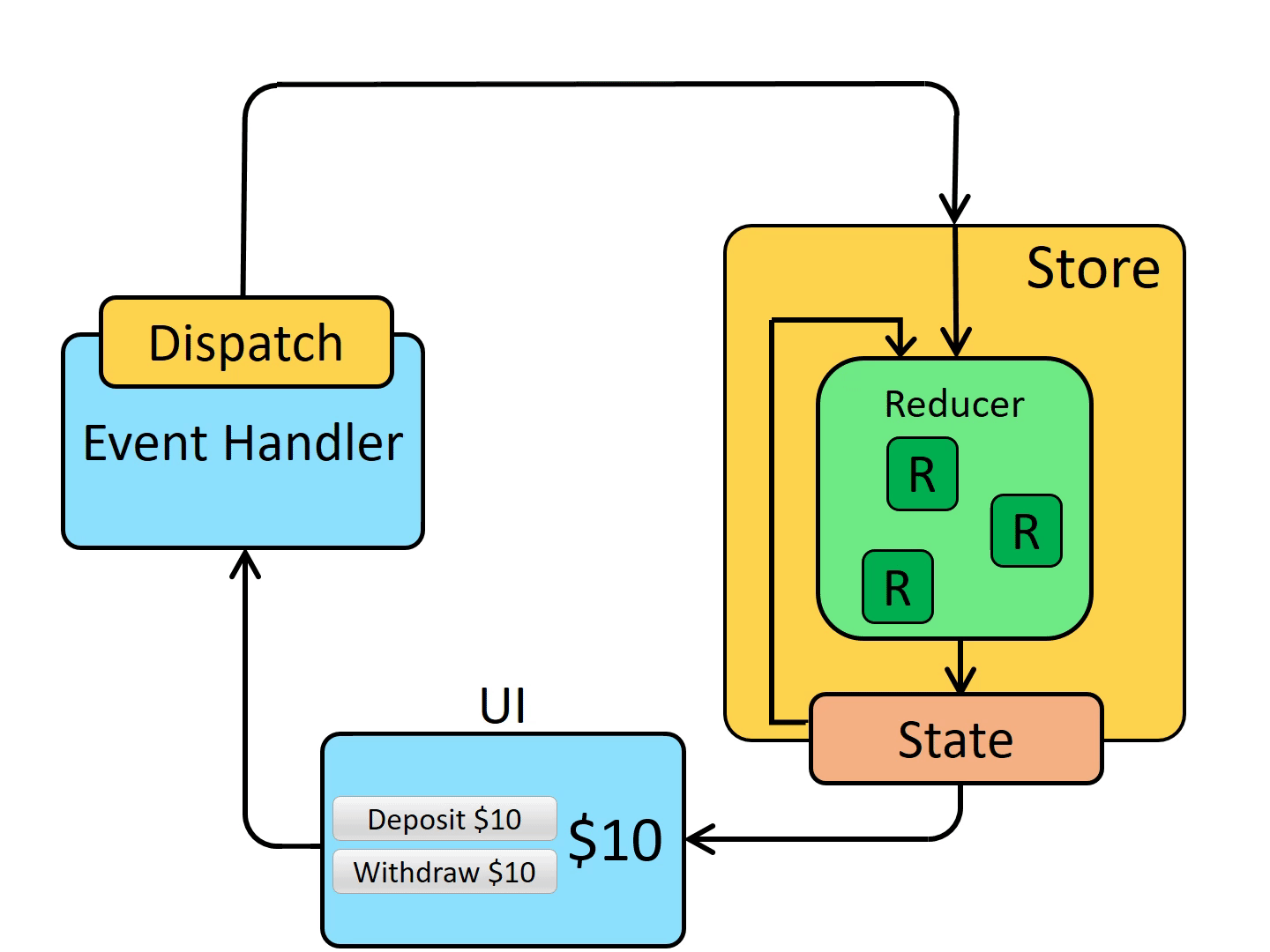
相关插件的使用
react-redux 用于状态管理的基本功能
redux-undo 状态管理中用于实现 撤销、恢复功能
@reduxjs/toolkit 配套 react-redux 用于状态管理
关于 react 中 hooks 的命名
useLoad 开头
通常用于 ajax 请求获取数据
useGet 开头
通常用于获取前端 redux 信息
文件中 引入的先后顺序
顺序
第三方插件往前面放,自定义插件往后面放
// 第三方插件
import React from 'react'
import { createBrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
// 自定义插件 (hook)
import MainLayout from '../layouts/MainLayout'
import ManageLayout from '../layouts/ManageLayout'
import QuestionLayout from '../layouts/QuestionLayout'
import Home from '../pages/Home'
import Login from '../pages/Login'